Ace Tips About How To Compensate Voltage Drop
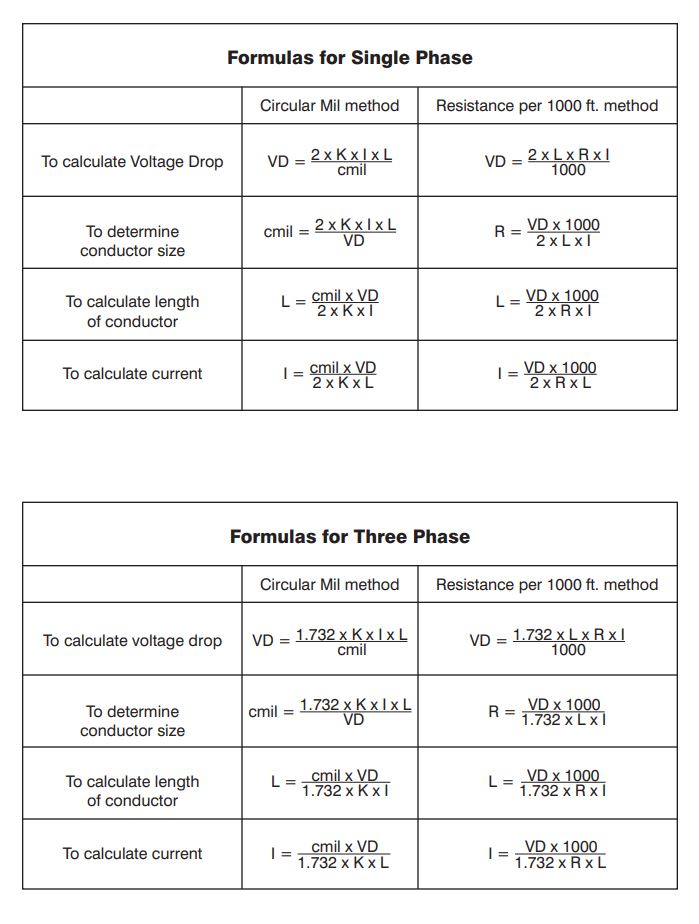
How To Calculate Resistance Needed For Voltage Drop At Lucille Ritter Blog
Understanding Voltage Drop
1. What Exactly Is Voltage Drop, Anyway?
Ever noticed how your lights dim slightly when you turn on the vacuum cleaner? That's voltage drop in action. Simply put, it's the decrease in electrical potential (voltage) along a conductor, like a wire, as the current flows through it. Think of it like water flowing through a pipe — the further it travels, the more pressure it loses due to friction. With electricity, the 'friction' comes from the resistance of the wire itself.
This resistance isn't necessarily a bad thing; it's inherent in all materials. However, excessive voltage drop can lead to all sorts of problems. It can make your appliances work less efficiently, cause lights to flicker, and even damage sensitive electronic equipment. Imagine trying to bake a cake with an oven that's not getting enough power — disaster!
So, where does voltage drop come from? Several factors contribute, including the length of the wire (longer wires mean more resistance), the wire gauge (thinner wires have higher resistance), and the amount of current flowing through the wire (more current, more drop). It's a delicate balancing act, and understanding these factors is the first step in keeping your electrical system happy and healthy.
Think of it like this: your electrical system is a circulatory system, and voltage is the blood pressure. Too much pressure is bad, but too little is equally problematic. Maintaining that sweet spot is key to smooth and efficient operation. And, let's be honest, nobody wants their electronics to feel like they're running a marathon uphill.

The Ramifications of Ignoring Voltage Drop
2. Why Should You Care About a Little Voltage Drop?
Okay, so your lights dim a little. Big deal, right? Wrong! Ignoring voltage drop can lead to a cascade of issues, some of which can be quite costly. Let's explore why it's crucial to keep a close eye on this electrical gremlin.
First off, reduced efficiency. Imagine your refrigerator struggling to keep things cold because it's not getting the full voltage it needs. It'll draw more current to compensate, leading to higher energy bills and a shorter lifespan for the appliance. Its like making your car work harder just to maintain the same speed.
Then there's the risk of equipment damage. Sensitive electronics, like computers and audio equipment, are particularly vulnerable to voltage fluctuations. A sudden drop can cause them to malfunction or even fail completely. And let's be real, replacing a blown-out motherboard is nobody's idea of a fun weekend project.
Finally, there's the safety aspect. Excessive voltage drop can cause wires to overheat, increasing the risk of fire. It might start as a barely noticeable warm spot, but over time, that heat can degrade the insulation and create a dangerous situation. So, tackling voltage drop isn't just about saving money; it's about protecting your home and your family.
Practical Solutions
3. Strategies to Combat Voltage Sag
Alright, you're convinced that voltage drop is something to take seriously. Now, let's get down to the good stuff: how to actually compensate for it. There are several effective strategies you can employ, depending on the specific situation.
One of the most common solutions is to increase the wire gauge. Remember, thicker wires have lower resistance, which means less voltage drop. It's like upgrading to a wider pipe for your plumbing — more flow with less pressure loss. Check the wire size and determine if it meets the current load requirements. If the wiring is underrated, it's time for an upgrade to eliminate the voltage drop issues.
Another tactic is to shorten the length of the wire run. Obviously, this isn't always possible, but if you can relocate the power source or the load closer together, you'll significantly reduce voltage drop. Think of it as taking a shortcut instead of a long detour — less distance to cover.
Increasing the voltage at the source can also help. For example, using a transformer to step up the voltage before sending power over a long distance can minimize losses. This is a common practice in power transmission lines, where voltages can reach hundreds of thousands of volts. It is however something that should be done by a professional to not overload anything!
Finally, consider using dedicated circuits for high-demand appliances. This prevents them from drawing excessive current from shared circuits, which can exacerbate voltage drop. It's like giving your washing machine its own personal power supply, so it doesn't have to compete with the hairdryer for electricity.

Calculating Voltage Drop In A Dc Circuit
Tools and Techniques for Measuring Voltage Drop
4. Putting Your Multimeter to Work
Before you start tearing into your wiring, it's helpful to actually measure the voltage drop to get a sense of the problem's severity. This requires a simple tool called a multimeter, which can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
To measure voltage drop, you'll need to take voltage readings at both the source (e.g., the circuit breaker) and the load (e.g., the appliance). Be sure to turn on the load, so it's drawing current. The difference between the two readings is the voltage drop. Remember to always use caution when working with electricity and turn off the breaker if you are not certain what you are doing.
Ideally, the voltage drop should be within a certain percentage of the source voltage. Electrical codes typically specify maximum allowable voltage drops, usually around 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders. Exceeding these limits indicates a problem that needs to be addressed. Measuring these things is something a professional is trained to do safely.
You can also use online voltage drop calculators to estimate the expected voltage drop based on wire gauge, length, and current. These calculators can be a useful tool for planning new circuits or troubleshooting existing ones. Remember to input the correct values, and they'll provide a valuable reference point. And be sure that you are always safe when messing with electricity.
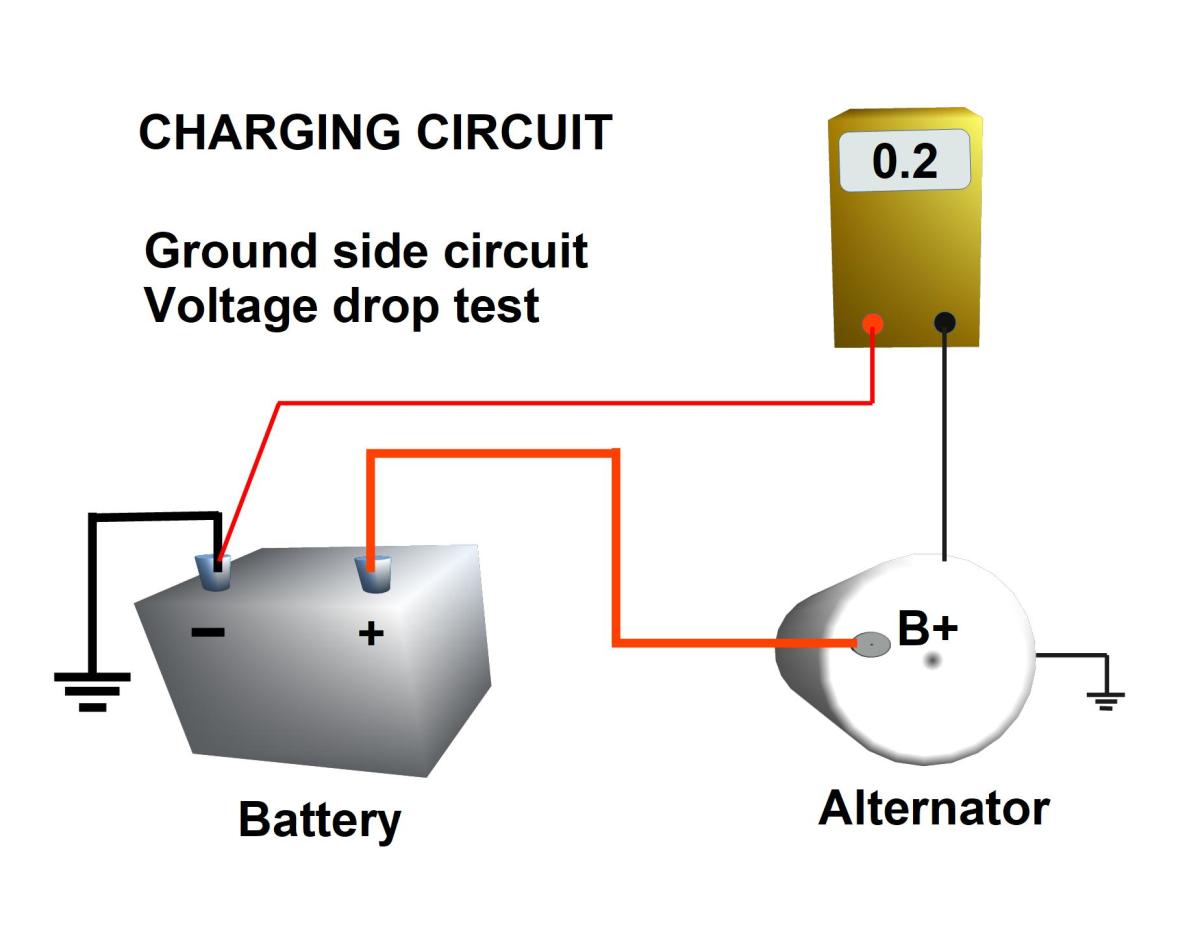
How To Do A Voltage Drop Test On Your Charging System HubPages
Maintenance and Prevention
5. Proactive Measures for a Healthy Electrical System
Compensating for voltage drop isn't just a one-time fix; it's an ongoing process. Regular maintenance and preventative measures can help keep your electrical system running smoothly and prevent future problems.
Periodically inspect your wiring for signs of damage, such as frayed insulation or loose connections. Tighten any loose connections, as they can increase resistance and contribute to voltage drop. It's like giving your car a regular tune-up to keep it running efficiently.
Avoid overloading circuits by plugging too many devices into a single outlet. This can draw excessive current and exacerbate voltage drop. Consider using power strips with surge protection to distribute the load more evenly. Just make sure that these power strips are also heavy-duty, for handling the amount of current you'll be passing through them.
If you're planning any new electrical work, consult with a qualified electrician to ensure that the wiring is properly sized for the load. They can also advise you on the best strategies for minimizing voltage drop in your specific situation. Because even though electricity is something that makes our lives easier, it can be dangerous when not used properly.
Upgrade older wiring, if you have some, and especially in older houses. Old wiring can often have deteriorated insulation, higher resistance, and all sorts of possible problems. This isn't always necessary, but it's a good idea to have it inspected from time to time.
+in+the+circuit+of+following+Figure.+Show+how+to+connect+a+voltmeter+to+measure+each+unknown+voltage+drop..jpg?strip=all)
How To Determine Voltage Drop In A Circuit Diagram
FAQ
6. Your Voltage Drop Queries, Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about voltage drop to further clarify the topic:
Q: What is the ideal voltage drop percentage?A: Generally, a voltage drop of no more than 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders is recommended to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Q: Can voltage drop damage appliances?A: Yes, excessive voltage drop can cause appliances to work harder, overheat, and potentially fail prematurely.
Q: Is voltage drop the same as power outage?A: No, voltage drop is a reduction in voltage, while a power outage is a complete loss of power. Voltage drop can result in appliances that operate poorly, while a power outage will prevent anything from working.
Q: I'm not an electrician. Can I fix voltage drop problems myself?A: While some minor issues might be addressed with basic knowledge, it's always best to consult a qualified electrician for any significant electrical work, because electricity can be dangerous when not used properly.